
Earth’s inner core is an incredibly fascinating and mysterious part of our planet. It is located at the center of the Earth, about 6,371 km below the surface and is made up of solid iron and nickel. Despite its immense size and density, scientists have only been able to study the inner core indirectly through seismic waves. Due to its extreme pressure and temperature, little is known about its composition, structure, and even its rotation. However, there are some interesting facts about Earth’s inner core that are worth exploring. In this article, we will explore some of these facts and discuss how they can help us better understand our planet. For more visit our interesting facts about earths crust post.
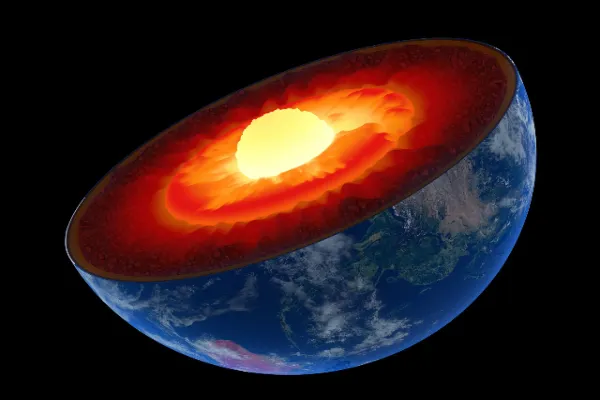
Uncovering the Secrets of Earth’s Inner Core
Earth’s inner core is an enigma that has puzzled scientists for centuries. The solid core of our planet lies at the center of the Earth and is roughly the size of Mars. This mysterious region is surrounded by a molten outer core, which is composed of iron and nickel and is 2,200 kilometers thick.
The inner core has been difficult to study due to its extreme temperatures and pressures. Scientists believe that temperatures inside the inner core may reach up to 5,400 degrees Celsius and pressures could be as high as three million times the pressure of Earth’s atmosphere.
In order to gain a better understanding of the inner core, scientists have employed a variety of techniques. Seismic waves, for example, are used to study the structure of the Earth’s interior. By analyzing the way these waves travel through the Earth, scientists can gain insight into the composition and structure of the inner core.
In addition, scientists have used mathematical models to simulate conditions inside the inner core. These models can help to provide an estimate of the temperature and pressure within the inner core.
The inner core is also studied through the study of iron meteorites. These meteorites are believed to have originated from the core of a planet similar to Earth. By analyzing the composition of these meteorites, scientists can gain insight into the composition of Earth’s inner core.
Despite these efforts, the inner core remains an enigma. Scientists continue to work to uncover the secrets of this mysterious region in order to better understand the structure and composition of our planet.
Fascinating Facts About Earth’s Inner Core
Earth’s inner core is a fascinating scientific phenomenon. It is the innermost layer of the Earth and is composed of solid iron and nickel, with temperatures estimated to be in excess of 5,000 degrees Celsius. It has an estimated radius of 1,220 kilometers and is the densest layer of the Earth, making up around 30% of the Earth’s total mass.
The inner core is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field. It is believed to be composed of aligned microscopic iron crystals, which are in constant motion due to convection currents caused by heat rising from the Earth’s core. This dynamic motion produces an electric current, which generates the Earth’s magnetic field.
The inner core is also believed to be the source of seismic waves, which are generated by earthquakes. Seismic waves travel through the Earth’s mantle and outer core before reaching the inner core. The inner core’s composition and structure affect the speed and absorption of seismic waves, providing important information about the Earth’s interior.
The inner core is still largely mysterious, and scientists continue to uncover new information about its composition and structure as they strive to gain a better understanding of the Earth’s interior.
Despite its small size, the inner core plays a vital role in understanding the structure and composition of the Earth and its importance to the Earth’s overall dynamics is undeniable.
What We Know About the Earth’s Inner Core
The Earth’s inner core is the innermost layer of the Earth, located at the center of the planet. It is the source of the Earth’s magnetic field and is composed of solid iron and nickel, with an estimated temperature of around 5,400°C (9,700°F). The inner core is believed to have a diameter of about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles) and is thought to have a density of about 13 times that of water.
The Earth’s inner core is thought to be a solid ball of iron and nickel, surrounded by an outer core composed of liquid iron and nickel. This liquid outer core is believed to be responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field. The inner core is believed to be the source of the Earth’s thermal energy, which is released through the Earth’s mantle. This thermal energy is thought to be responsible for the Earth’s tectonic activity.
Despite its small size, the inner core is of great scientific significance. Its composition and structure are thought to be important for understanding the Earth’s magnetic field and its tectonic activity. Additionally, the inner core is believed to be a major source of the Earth’s seismic activity.
The inner core is too deep and too hot for direct observation, so scientists study it indirectly, using seismic waves. The seismic waves travel through the Earth’s mantle and core, and they can be used to infer the structure and composition of the inner core.
The inner core is an important part of the Earth, and its structure and composition are of great scientific interest. With better understanding of the inner core, it may be possible to gain insights into the Earth’s magnetic field and tectonic activity, which could have implications for understanding the Earth’s climate.
Leave a Reply